On and Off Again Hpv Test
, by NCI Staff
UPDATE: On March 11, 2020, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) canonical the starting time dual-stain test for women who take tested positive for HPV. The test, called CINtec® PLUS Cytology, is used to assistance doctors decide if an HPV-positive woman should have a biopsy to look for cervical precancer or cancer.
A new test, called dual stain, may help improve how doctors intendance for women who test positive for human papillomavirus (HPV) infection during routine cervical cancer screening, an NCI-led study has shown. HPV tests detect infections with the cancer-causing types of HPV.
For most women, HPV infections go away on their own. Merely for some, the infection leads to precancerous growths that can progress to cervical cancer. To better care for women who are HPV positive, researchers take been exploring means to aid tell whether an HPV infection is likely to cause precancer.
As HPV testing becomes a more mutual method of cervical cancer screening, "the challenge is how to best manage, or triage, HPV-positive women," said the study's senior investigator, Nicolas Wentzensen, 1000.D., Ph.D., of NCI'due south Division of Cancer Epidemiology and Genetics (DCEG).
Doctors usually use a Pap exam, besides called a Pap smear, to determine whether an HPV infection is probable to crusade precancer and help decide whether a adult female should go a biopsy. But, according to the NCI study, the dual-stain test was ameliorate than the Pap examination at predicting whether HPV-positive women developed cervical precancer inside 5 years.
The findings suggest that HPV-positive women with a positive dual-stain test result should get a biopsy to check for cervical precancer or cancer, the study authors concluded, whereas those with a negative event can safely await 3 years before getting screened again. Results from the prospective written report were reported October xi in JAMA Oncology.
"This is a very important report," said Mark Stoler, M.D., associate director of Surgical Pathology and Cytopathology at the University of Virginia School of Medicine. It's the start study performed in the United States, Dr. Stoler connected, "that really provides the assurance that [dual stain] is a better triage test" than the Pap test.
Cervical Cancer Screening in the United States
At that place are around 12 dissimilar types of HPV that tin can crusade cervical and other types of cancer. HPV infections that aren't controlled by the immune arrangement are the cause of almost all cervical cancers. Cervical cancer screening tests expect for disease in people who have no symptoms.
Electric current US guidelines for cervical cancer screening recommend ane of iii approaches: an HPV examination lone, a combination of HPV and Pap tests (an HPV/Pap cotest), or a Pap test solitary.
According to the United states of america Preventive Services Chore Strength, women age thirty to 65 years at average take chances of cervical cancer tin exist safely screened with an HPV test or HPV/Pap cotest every 5 years.
Although HPV/Pap cotesting has improved the accurateness of cervical cancer screening and helped to profoundly reduce the incidence of cervical cancer, information technology has some limitations.
For example, some women who examination positive for HPV and who take minor abnormalities on a Pap test are referred for colposcopy, a procedure in which biopsies are taken of aberrant areas in the neck (visit NCI's page on cervical screening tests for the almost upwards-to-date recommendations).
But only a small pct of Pap test abnormalities plough out to be cervical precancer or cancer, meaning nearly of these women had an unnecessary colposcopy, Dr. Wentzensen explained. Considering of these limitations, "there is a big effort to find better markers that permit us to triage HPV-positive women more than efficiently," he said.
In terms of potential triage approaches for HPV-positive women, dual-stain testing "is probably the most advanced method available," said the study's pb investigator, Megan Clarke, Ph.D., Thousand.H.S., too of DCEG. The new study adds to that body of evidence, she said.
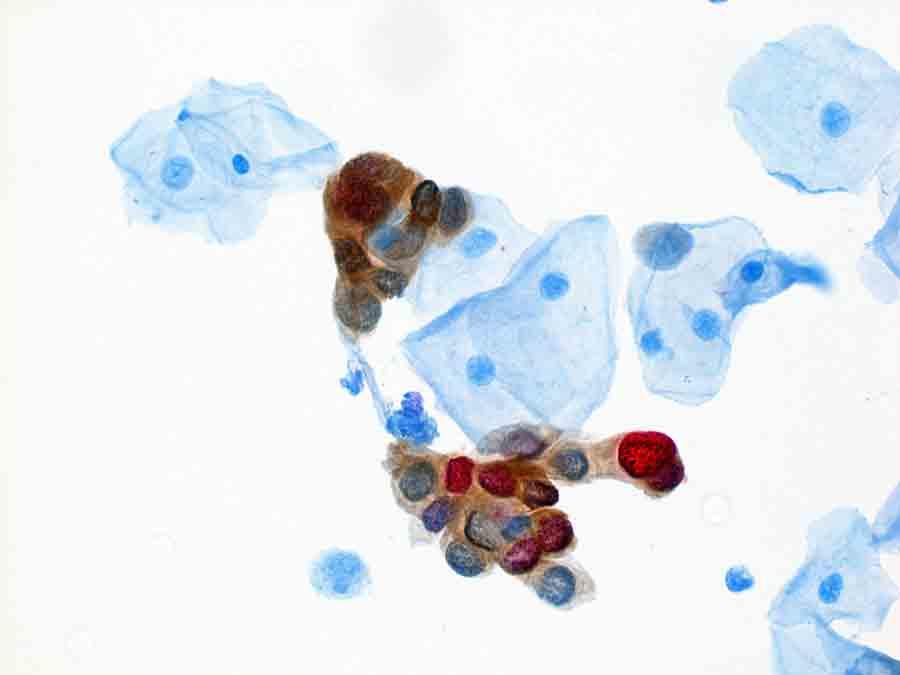
The dual-stain arroyo has been under study for more a decade, Dr. Stoler said. It measures the presence of two specific proteins, p16 and Ki-67, in a sample of cervical cells. The expression of p16 is strongly linked with HPV infection, and Ki-67 is used as a biomarker for the rapid cell division seen in precancers and cancer.
Previous studies take provided some show that dual-stain testing is amend at identifying HPV-positive women who have precancers than Pap testing, but none followed patients forward in time for more than three years.
Searching for a Better Triage Exam for HPV-Positive Women
To comport this new study, the investigators followed 1,549 women aged 30 or older who had tested positive for HPV (on a exam that gives combined results for xiii cancer-causing types) while undergoing routine HPV/Pap cotesting at Kaiser Permanente Northern California betwixt Jan and May 2012. Dual-stain testing was performed on participants' cervical cell samples at the beginning of the study.
Women with a normal Pap examination result were advised to repeat the cotest in one year, whereas women with an abnormal result were referred for immediate colposcopy and biopsy. Biopsy results can reveal a range of illness states, including normal, low-course to loftier-form precancer, and cancer.
Overall, 46% of women in the study had a positive dual-stain test consequence and 51% had an aberrant Pap examination issue. More women with severely abnormal Pap test results than women with normal Pap results had a positive dual-stain test consequence. Over the 5-yr study period, 77% of women found to have a high-course precancer and 91% found to have cancer had a positive dual-stain test issue.
Compared with Pap examination results, dual-stain test results were far more indicative of the 5-year adventure of cervical precancer, the team found. For instance, women with a positive dual-stain test consequence had a higher adventure of developing cervical precancer over the next v years than women with a positive Pap examination issue.
Conversely, women with a negative dual-stain test result had a lower hazard of developing cervical precancer within 5 years, compared with women with a normal Pap test result.
This means that a negative dual-stain examination result gives greater reassurance than a normal Pap exam issue that precancer won't develop during the ensuing 5 years, Dr. Wentzensen explained.
Dr. Clarke said that the study as well addressed a critical question: "How oft and at what time interval should HPV-positive women who test negative with dual stain come back for echo screening?"
Based on the 5-year risks of cervical precancer, the researchers determined that HPV-positive women with a negative dual-stain upshot can safely wait 3 years before beingness screened over again.
Together, the findings propose that using the dual-stain test to triage HPV-positive women might lead to fewer unnecessary colposcopies, Dr. Clarke noted.
The higher sensitivity (i.eastward., better at identifying women with a higher take chances of having precancer) and specificity (i.e., ameliorate at identifying those with a depression hazard) of the dual stain-test compared with the Pap test is impressive, Dr. Stoler said.
"Information technology's very hard to take a test that improves sensitivity and specificity, simply dual stain does it because of the biology backside the development of the exam," he explained.
Learning More than About Dual Stain
The dual-stain test is already beingness marketed and used in several countries, including Canada, Europe, and Commonwealth of australia, Dr. Stoler said. The clinical trial that would form the basis of FDA clearance for the dual-stain test in the United States is currently ongoing, he added.
In the hereafter, HPV testing followed by dual stain for primary cervical cancer screening may exist a more efficient culling to HPV/Pap cotesting, Drs. Wentzensen and Clarke said.
The manufacturer of the dual-stain exam is analyzing the development of cervical precancer in HPV-positive women who have a positive test result from either dual stain or Pap in an ongoing study. In addition, Dr. Wentzensen and his colleagues are investigating the results of dual stain testing in a large population of women, including many who are HPV negative.
"I call back there volition be sufficient data to change practice based on these observational studies," said Dr. Wentzensen.
And the test may before long have other attractive qualities, the investigators noted. A major advantage of the dual-stain examination, said Dr. Wentzensen, is that aberrant cells are highlighted with a colored stain and are therefore easier to detect and quantify than cells stained for a Pap test.
"Currently, the dual-stain test is evaluated manually, but we are working on an automated evaluation of this analysis and we take heady results," he added. Automation of the dual-stain test would enhance its reliability and make it easier to use, he said.
Source: https://www.cancer.gov/news-events/cancer-currents-blog/2018/dual-stain-test-cervical-hpv-positive
Post a Comment for "On and Off Again Hpv Test"